Eureka: Intelligent Feature Engineering for Enterprise AI Cloud Resource Demand Prediction
About Eureka
Eureka is an agentic feature engineering framework that discovers high-quality, interpretable features—even under data scarcity—across LLM and VLM applications. It consists of three components:
- Eureka Expert (Planning Stage) encodes domain knowledge as heuristic constraints and design templates to guide exploration of feature interactions and cross-resource dependencies. It steers toward domain-meaningful candidates, filters spurious correlations, and identifies high-order feature dependencies that reflect system dynamics.
- LLM Feature Factory (Execution Stage) translates design plans into concrete features via conditioned code generation. Guided by domain heuristics, it explores the feature space and outputs executable implementations that maximize information signal from limited historical data.
- Self-Evolving Alignment Engine (Refinement Stage) improves feature quality using dual-channel reward feedback from real-world deployment outcomes. By linking offline optimization with online performance, it adapts features to irregular workload patterns while preventing overfitting.
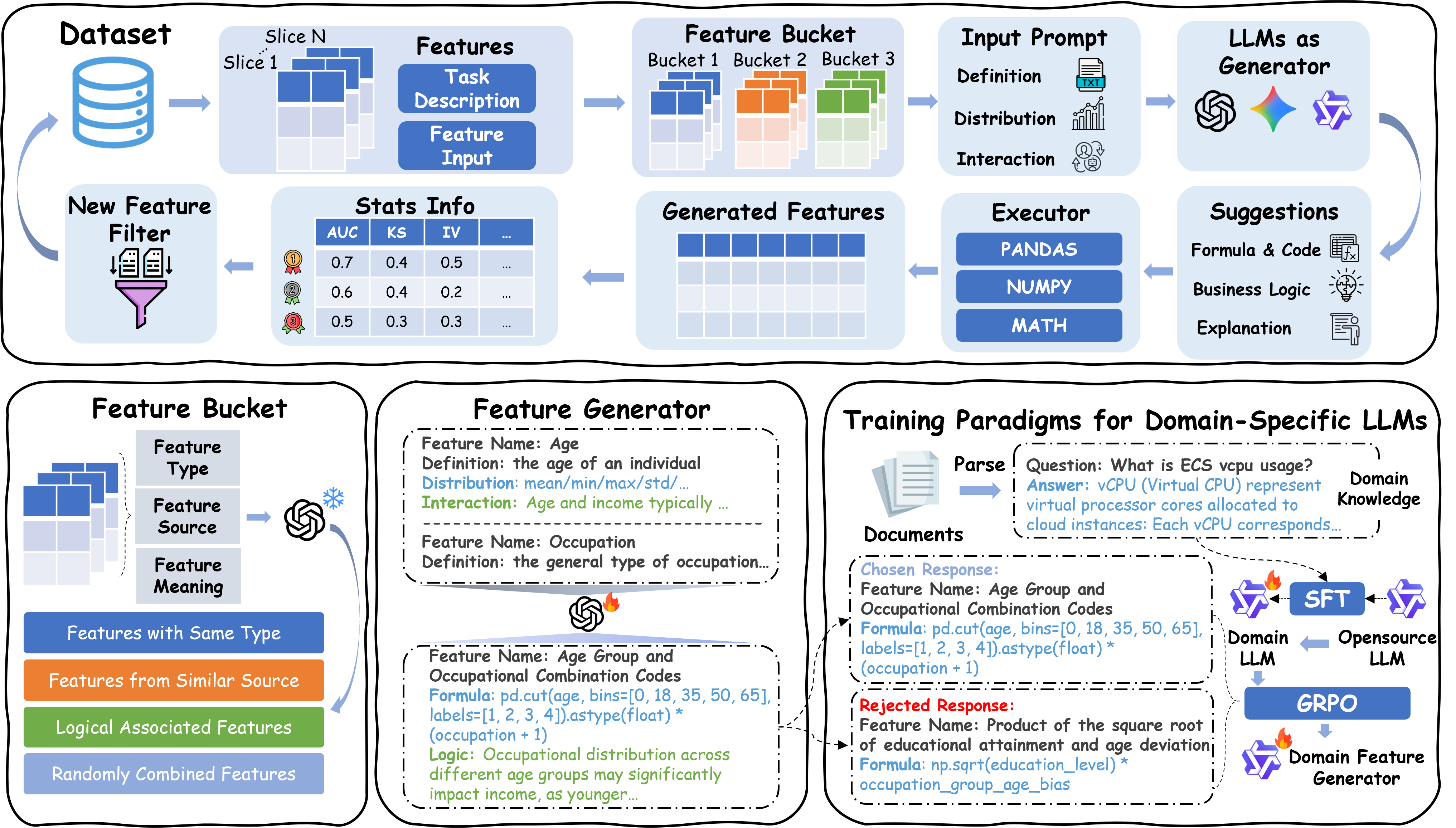
Generate high-quality features with Eureka
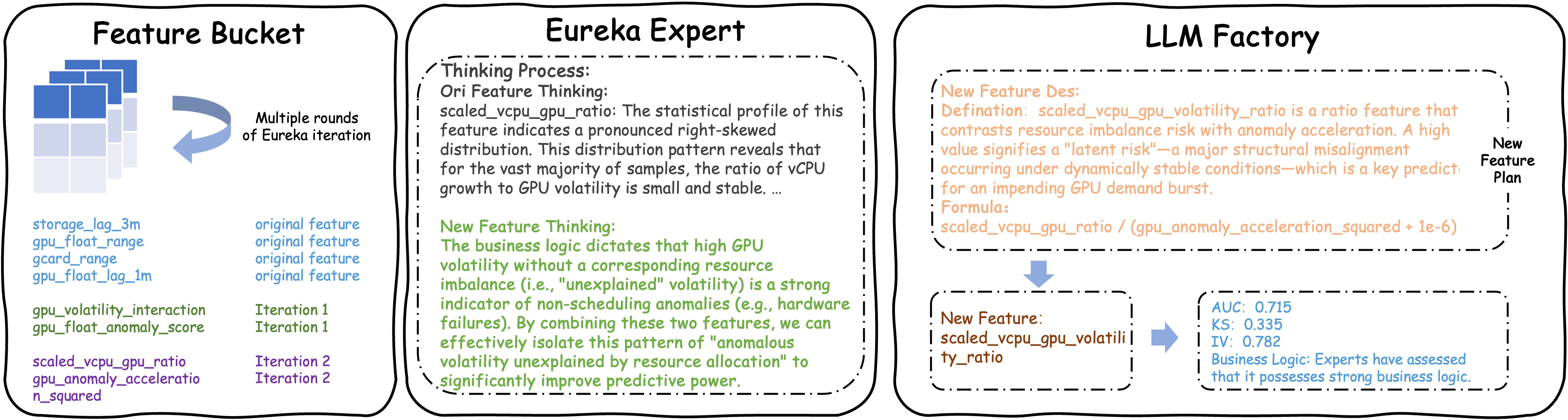
To show Eureka’s real-world value, consider the production case shown in the figure above: it successfully caught a GPU demand surge that traditional monitoring systems completely missed. Here’s how it worked. At first glance, two raw signals—gpu_anomaly_acceleration_squared and scaled_vcpu_gpu_ratio—looked weak and uninformative on their own, so a standard pipeline would’ve thrown them out. But Eureka’s domain expert module saw something deeper. It knows that large AI training jobs don’t just start out of nowhere—they’re usually preceded by a “prep phase,” where customers quietly spin up vCPUs, set up data pipelines, and provision storage before firing up GPUs. That means a temporarily high vCPU-to-GPU ratio isn’t a bug—it’s actually a sign of preparation!
Eureka reinterpreted this as a “preparatory imbalance”—a subtle but reliable early warning. Guided by this insight, its LLM-powered feature factory generated new candidates, and after validation by the self-evolving engine, it zeroed in on a smart new feature: scaled_vcpu_gpu_volatility_ratio. This feature essentially divides the prep signal (high vCPU/GPU ratio) by a near-zero GPU acceleration value (meaning GPUs are still idle), which amplifies the “calm before the storm.” In practice, this new metric spikes days before actual GPU demand peaks—while all conventional metrics stay flat—giving operators enough lead time to act. Thanks to this, Eureka didn’t just predict the burst; it explained why it was coming.
Experimental Results
To evaluate Eureka’s effectiveness, we test it on multiple public classification datasets as well as an internal enterprise dataset from Alibaba Cloud. The results are summarized below.
Performance Comparison Across Different Methods and Datasets
| Method | Adult | Bank | Blood | Credit | Diabetes | Heart | Myocardial | EGS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DFS | 0.915 | 0.897 | 0.637 | 0.707 | 0.882 | 0.921 | 0.654 | 0.680 |
| AutoFe | 0.872 | 0.865 | 0.735 | 0.676 | 0.837 | 0.903 | 0.674 | 0.666 |
| OpenFe | 0.920 | 0.923 | 0.626 | 0.701 | 0.817 | 0.897 | 0.697 | 0.658 |
| TabPFN | 0.900 | 0.904 | 0.715 | 0.787 | 0.888 | 0.938 | 0.676 | 0.694 |
| CAAFE | 0.901 | 0.905 | 0.713 | 0.797 | 0.886 | 0.941 | 0.686 | 0.692 |
| FeatLLM | 0.894 | 0.851 | 0.678 | 0.743 | 0.811 | 0.881 | 0.663 | 0.675 |
| Eureka-Qwen | 0.926 | 0.932 | 0.738 | 0.794 | 0.873 | 0.926 | 0.737 | 0.679 |
| Eureka-32B | 0.926 | 0.932 | 0.716 | 0.824 | 0.884 | 0.936 | 0.711 | 0.688 |
| Eureka-gpt4o | 0.928 | 0.934 | 0.745 | 0.838 | 0.881 | 0.938 | 0.699 | 0.699 |
| Eureka-grok2 | 0.928 | 0.934 | 0.735 | 0.815 | 0.886 | 0.940 | 0.719 | 0.686 |
The results reveal several key insights. The proposed Eureka framework consistently achieves strong and superior performance across multiple datasets, particularly excelling on feature-rich data such as Myocardial. This advantage stems from Eureka’s ability to semantically interpret original features and generate domain-informed feature combinations, which is especially beneficial in complex, high-dimensional settings. Eureka-Qwen, Eureka-grok2, and Eureka-gpt4o utilize corresponding proprietary APIs, while Eureka-32B is a fine-tuned open-source variant based on Qwen3-32B. Among them, Eureka-gpt4o attains the highest accuracy on four datasets (Adult, Bank, Blood, and Credit-g) and remains competitive elsewhere. Eureka-Qwen leads on Myocardial (0.737), highlighting its strength in handling feature-rich data, while Eureka-grok2 performs best on Heart and shows strong results on Adult and Bank. Overall, the consistent superiority of Eureka demonstrates the framework’s effectiveness and generalization ability in automated feature engineering.
BibTeX
@inproceedings{
li2025eureka,
title={Eureka: Intelligent Feature Engineering for Enterprise {AI} Cloud Resource Demand Prediction},
author={Hangxuan Li and Renjun Jia and Xuezhang Wu and zeqi zheng and Yunjie Qian and Xianling Zhang},
booktitle={1st Workshop on VLM4RWD @ NeurIPS 2025},
year={2025},
url={https://openreview.net/forum?id=zeTzKZezXY}
}